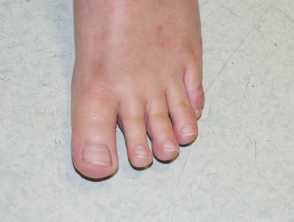
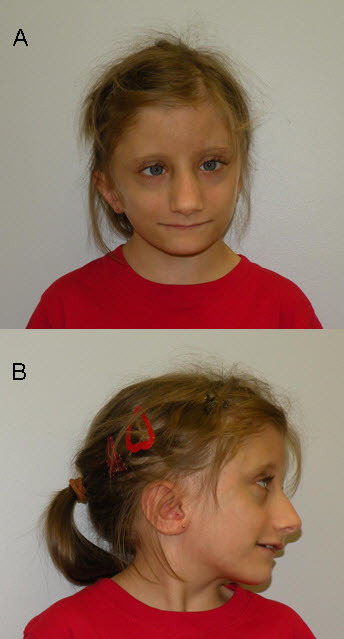
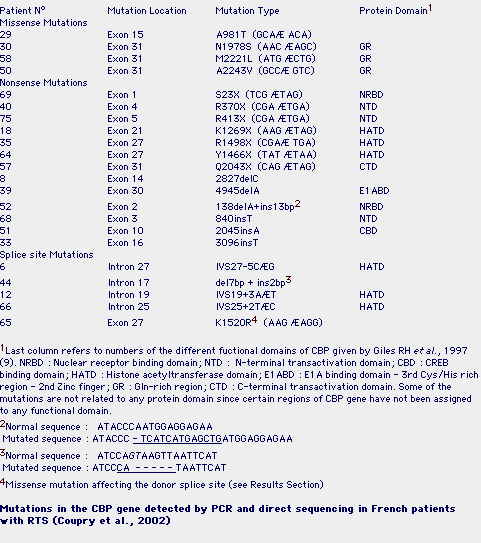
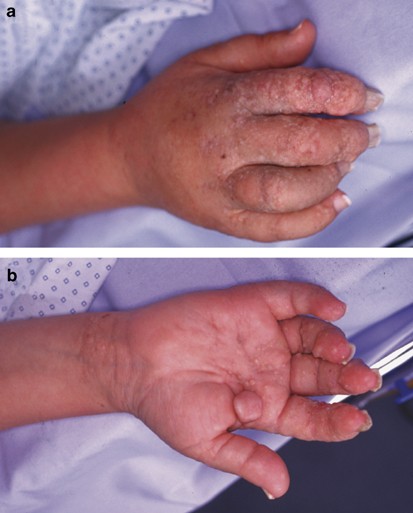
(PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation and epidermal nevus (SOLAMEN) syndrome is related to mosaic PTEN nullizygosity
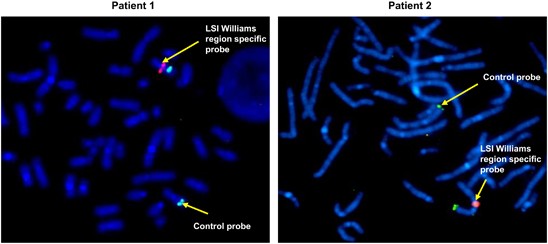
Functional and genetic characterization of two extremely rare cases of Williams–Beuren Syndrome associated with chronic granulomatous disease

PDF) De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia

Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Deficiency in Bone Marrow–Derived Cells Augments Rupture of Angiotensin II–Induced Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
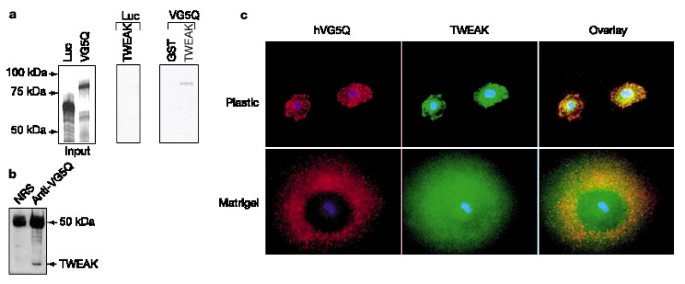
Identification of an angiogenic factor that when mutated causes susceptibility to Klippel–Trenaunay syndrome
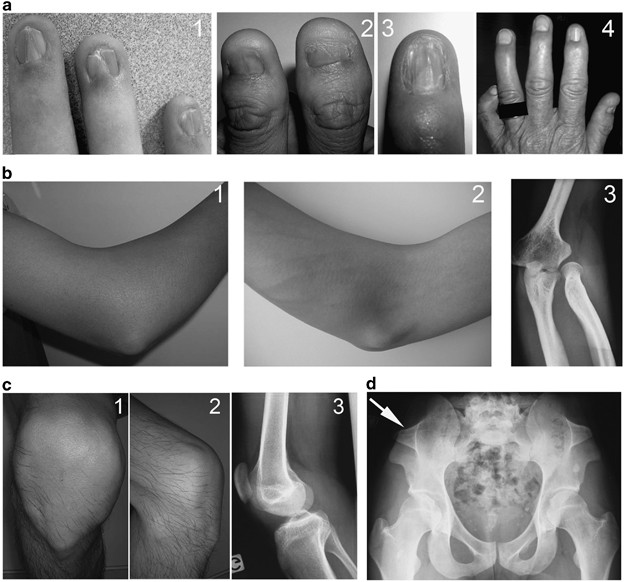
Nail–Patella Syndrome: clinical and molecular data in 55 families raising the hypothesis of a genetic heterogeneity

PDF) Generation of the Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome type 2 patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cell line (IAIi001-A) carrying the EP300 exon 23 stop mutation c.3829A > T, p.(Lys1277*)

PDF) De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia
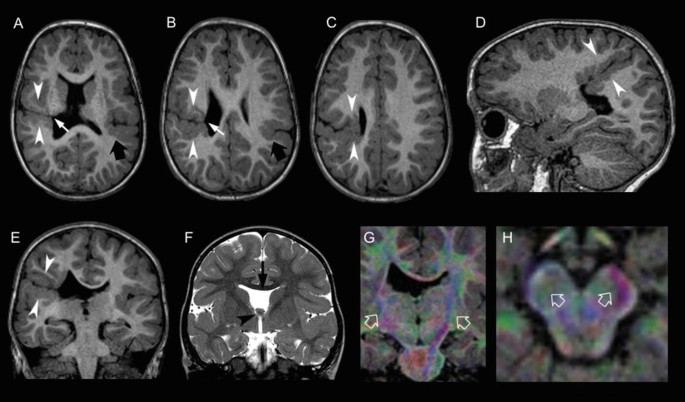
Malformations of Cortical Development
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)